SOLAR OFF-GRID&ON-GRID INVERTERS
Solar Off-Grid Inverters: Off-grid inverters are designed for use in standalone solar systems that operate independently from the main power grid. Their primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) electricity that can power household appliances and devices. These inverters are also responsible for managing the energy flow between the solar panels and the batteries used to store excess energy for use during periods of low solar production, such as at night or during cloudy days. Off-grid inverters need to be robust and reliable, as they play a critical role in maintaining the energy balance and stability of off-grid systems.
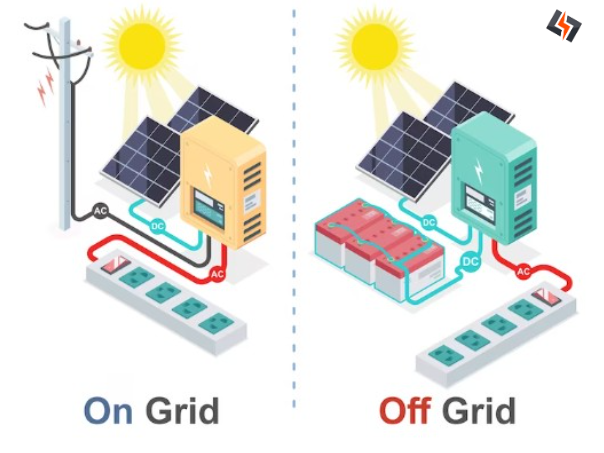
Solar On-Grid Inverters: On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, are used in solar systems that are connected to the main power grid. Their main purpose is to convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be either used to power local appliances or fed back into the grid. This latter process, known as net metering, allows you to earn credits for the excess electricity you produce, which can offset your electricity costs. On-grid inverters must be capable of synchronizing their output with the grid’s frequency and voltage to ensure a seamless integration of solar power into the overall grid supply. They do not include battery storage because they rely on the grid as the “virtual” storage system.
In summary, off-grid inverters are tailored for self-sufficient solar systems that operate independently of the grid and often include battery storage, while on-grid inverters are designed for solar systems that are connected to the main power grid and facilitate the interaction between solar-generated power and grid power.

